The metaverse, an emerging landscape of interconnected virtual worlds, presents a novel frontier for advertising. As these digital environments mature, businesses are exploring strategies to engage virtual audiences. Metaverse advertising companies specialize in developing and implementing these strategies, bridging traditional marketing principles with the unique characteristics of virtual space.
The metaverse advertising ecosystem is complex, encompassing a range of technologies, platforms, and user behaviors. Unlike conventional web advertising, where banners and pop-ups dominate, metaverse advertising frequently integrates into the virtual environment itself. This necessitates a different approach to campaign design and execution.
Key Players and Services
Metaverse advertising companies often provide a suite of services, from strategic consultation to technical implementation. These can include:
- Platform Selection Guidance: Advising clients on which metaverse platforms (e.g., Decentraland, The Sandbox, Roblox) align best with their marketing objectives and target demographics. Each platform has distinct technical capabilities, user bases, and commercial models.
- Virtual Asset Creation: Designing and developing branded virtual objects, wearables, and experiences. This might involve 3D modeling, texturing, and animation to ensure assets are both visually appealing and functional within the chosen metaverse.
- In-World Event Management: Organizing and promoting virtual concerts, product launches, or interactive experiences. These events can draw significant virtual attendance and offer unique opportunities for brand interaction.
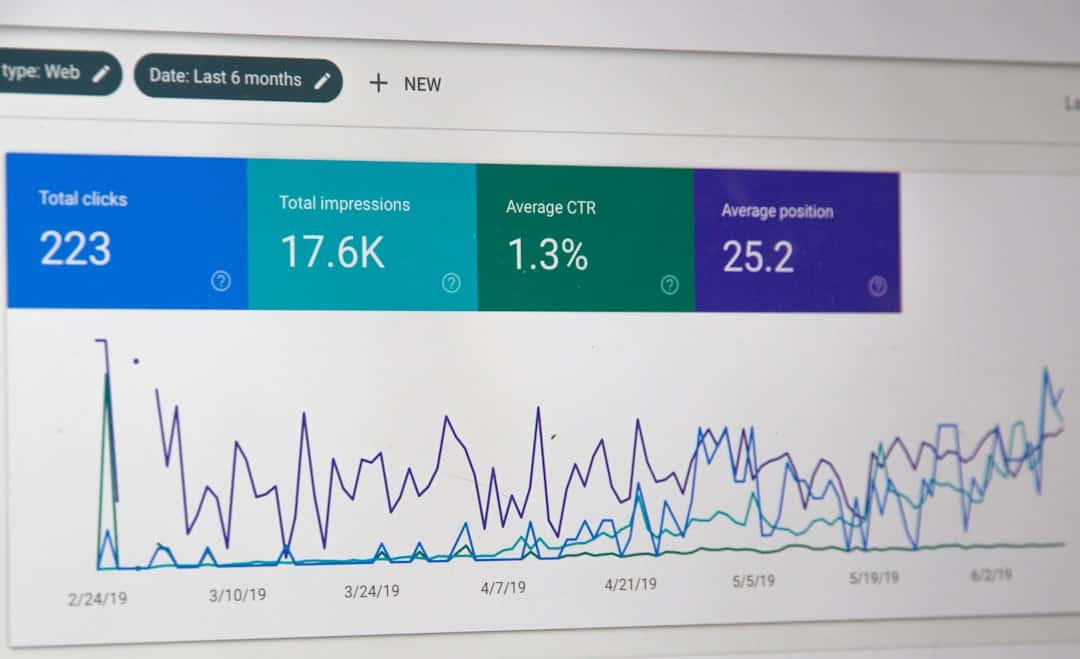
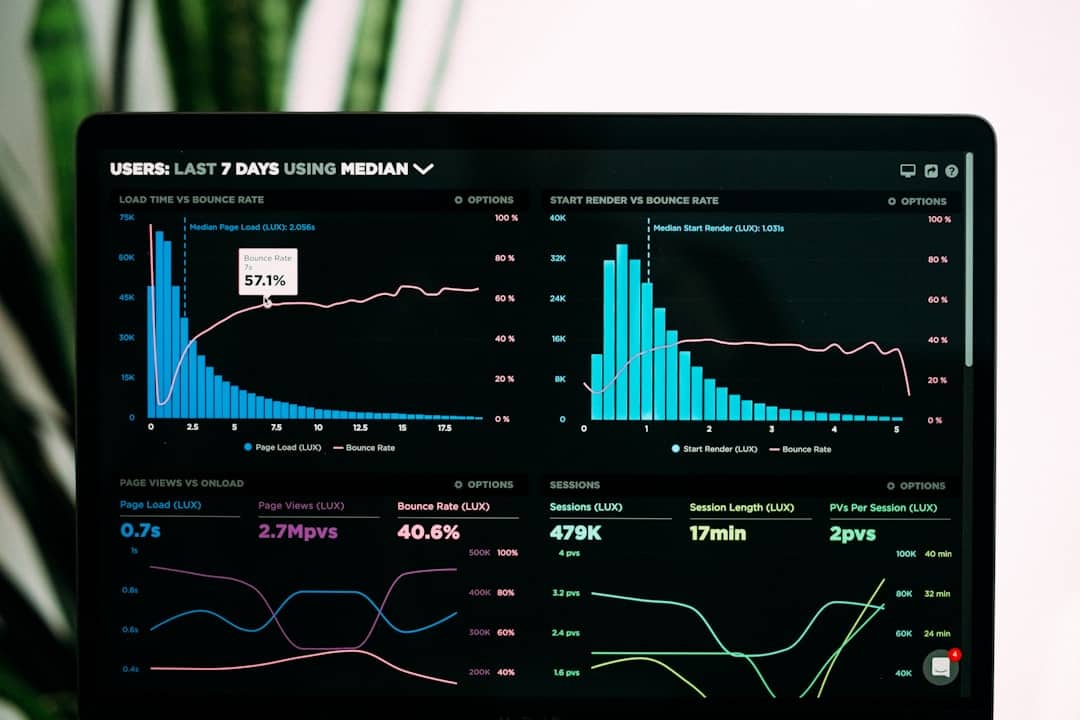
- Audience Data and Analytics: Tracking user engagement within virtual spaces to assess campaign effectiveness. This can involve analyzing virtual foot traffic, interaction rates with branded assets, and conversion metrics for in-world purchases or external website visits.
- Compliance and Legal Consultancy: Navigating the evolving legal and ethical landscape of virtual advertising, including issues of data privacy, intellectual property, and virtual goods ownership.
Challenges and Opportunities
The nascent state of the metaverse also presents both challenges and opportunities. Scalability remains a significant hurdle; replicating large-scale real-world advertising campaigns in a fragmented virtual environment requires sophisticated technical solutions. However, the opportunity for deep, immersive brand engagement is substantial, potentially fostering stronger brand loyalty than traditional advertising methods.
In the rapidly evolving landscape of digital marketing, metaverse advertising companies are at the forefront of innovation, creating immersive experiences that engage users in unprecedented ways. A related article that delves deeper into this topic is an insightful interview featured on Metaversum, which explores the strategies and challenges faced by these companies as they navigate the complexities of advertising within virtual environments. To read more about this fascinating subject, visit the article here: Metaversum Interview.
Advertising Formats and Approaches
Metaverse advertising deviates from traditional formats, often favoring integration over intrusion. This section explores common approaches used by companies operating in this space.
Immersive Experiences and Branded Worlds
Rather than merely placing advertisements, many brands create entire virtual experiences or dedicated brand worlds within the metaverse. This approach treats the brand as a destination rather than a message.
- Virtual Showrooms: Replicating real-world retail spaces in a virtual environment, allowing users to browse, interact with, and even purchase virtual or physical products. These showrooms can offer 3D models of products, interactive demonstrations, and direct links to e-commerce sites.
- Branded Games and Quests: Developing mini-games or narrative quests that incorporate brand elements or messaging. Users engage with these experiences, often receiving virtual rewards, which reinforces brand association. For example, a sports apparel company might create a virtual obstacle course where players wear branded avatars and compete for rewards.
- Event Sponsorship and Hosting: Sponsoring or hosting virtual concerts, fashion shows, or conferences within a metaverse platform. These events provide a captive audience for brand exposure and allow for interactive engagement through virtual merchandise or branded activities.
In-World Advertising Units
While more integrated, traditional advertising units still exist within the metaverse, often recontextualized for the virtual environment.
- Dynamic Virtual Billboards: Digital billboards placed within highly trafficked virtual areas. These can display static images, animated content, or even interactive elements. Unlike traditional billboards, virtual versions can be dynamic, changing content based on user demographics or real-time events.
- Product Placement within Games: Integrating branded virtual objects directly into user-created or platform-developed games. This can be subtle, such as a soda vending machine displaying a brand logo, or more prominent, like a car model from a specific manufacturer being drivable within the game.
- Avatar Wearables and Skins: Companies can design and distribute branded virtual clothing, accessories, or avatar skins. Users purchase or earn these items, effectively becoming walking advertisements within the metaverse. This fosters a sense of ownership and personal expression tied to the brand.
Technological Infrastructure for Metaverse Advertising
The underlying technology is the backbone of any metaverse advertising strategy. Companies in this sector invest in and leverage various tools and platforms.
3D Content Creation Tools
The visual fidelity of metaverse assets is paramount. Advertisers rely on advanced 3D modeling and animation software.
- Modeling Software: Industry-standard tools like Blender, Autodesk Maya, or 3ds Max are used to construct virtual objects, environments, and characters. These tools enable the creation of high-fidelity assets that can be optimized for various metaverse platforms.
- Texturing and Shading: Software like Substance Painter is essential for applying realistic textures and materials to 3D models, making them visually appealing and integrated into the virtual environment.
- Game Engines: Tools such as Unity and Unreal Engine are frequently employed for developing complex interactive experiences and branded virtual worlds. These engines provide robust frameworks for physics, lighting, and scripting, enabling dynamic and engaging content.
Blockchain and NFTs
Blockchain technology, particularly Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs), plays a role in establishing ownership and scarcity of virtual assets, impacting advertising and commerce.
- NFTs for Virtual Goods: Brands can leverage NFTs to create unique, verifiable virtual collectibles or merchandise. These NFTs can be sold, traded, or given away as promotional items, fostering a sense ofclusivity and digital ownership. This also allows for secondary markets, potentially extending brand reach and revenue streams.
- Token-Gated Experiences: Some metaverse experiences or product drops are accessible only to holders of specific NFTs. This creates an exclusive community and can be used as a loyalty program or a method to reward early adopters.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): While less direct in advertising, DAOs are emerging as governance structures within some metaverse platforms. Understanding these structures can be crucial for long-term influence and partnership strategies.
Analytics and Tracking Platforms
Measuring the effectiveness of campaigns in a real-time, interactive environment requires specialized analytics.
- In-World Analytics Tools: Proprietary platforms or third-party solutions designed to track user behavior within specific metaverse platforms. This includes metrics like avatar traffic, interaction time with branded objects, and conversion rates for virtual purchases.
- Cross-Platform Data Aggregation: As the metaverse fragments across multiple platforms, aggregating data from various sources becomes crucial for a holistic view of campaign performance. This helps advertisers understand overall reach and engagement across different virtual environments.
- Sentiment Analysis: Monitoring social media and virtual community discussions metaverses to gauge public perception of branded experiences. This provides qualitative data that complements quantitative metrics.
Strategic Planning and Implementation
Effective metaverse advertising requires a well-defined strategy, executed with precision. Companies in this sector guide clients through this process.
Defining Objectives and KPIs
Before any development begins, clear objectives must be established. This forms the bedrock of the advertising strategy.
- Brand Awareness: Increasing recognition of a brand within virtual communities. Metrics might include virtual billboard impressions or mention rates in metaverse forums.
- Customer Engagement: Fostering deeper interaction with a brand beyond passive viewing. This could involve tracking participation in virtual events or interaction with branded 3D objects.
- Lead Generation/Sales: Driving traffic to external e-commerce sites or facilitating in-world purchases of virtual goods. Conversion rates and return on ad spend (ROAS) are key metrics here.
- Community Building: Cultivating a loyal following within the metaverse. This might involve tracking active members in branded virtual spaces or participation in exclusive NFT drops.
Target Audience Identification
Understanding who you are trying to reach in the metaverse is critical. The demographics and psychographics of metaverse users can differ significantly from traditional online audiences.
- Platform-Specific Demographics: Each major metaverse platform often has a distinct user base. For example, Roblox tends to have a younger demographic, while Decentraland might attract more cryptocurrency enthusiasts.
- Behavioral Data: Analyzing how users interact within virtual worlds—what activities they engage in, what virtual goods they consume, and which communities they participate in—can inform targeting strategies.
- Psychographic Profiling: Understanding the motivations and desires of metaverse users, such as their interest in self-expression, community, or digital ownership.
Campaign Design and Execution
The design phase translates strategic objectives into tangible virtual experiences.
- Concept Development: Brainstorming creative ideas for virtual experiences, assets, and events that align with the brand’s identity and marketing objectives. This involves sketching, mood boards, and early 3D mockups.
- Technical Development and Integration: Working with 3D artists, developers, and platform specialists to build and deploy virtual assets and experiences optimizing for performance and user experience across various devices and network conditions.
- Promotion and Outreach: Utilizing traditional marketing channels, public relations, and in-metaverse advertising to promote virtual campaigns and events. This might involve metaverse influencers, community managers, and cross-platform partnerships.
As businesses increasingly explore the potential of virtual environments, the role of metaverse advertising companies becomes more significant. These companies are at the forefront of creating immersive marketing experiences that engage users in innovative ways. For a deeper understanding of how user-generated content is shaping community and culture in the metaverse, you can read this insightful article on the topic. It highlights the evolving landscape and the impact of user contributions on virtual marketing strategies. To learn more, visit this article.
The Future of Metaverse Advertising
| Company Name | Headquarters | Year Founded | Primary Platform | Ad Formats | Notable Clients | Annual Revenue (in millions) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meta (Facebook) | Menlo Park, USA | 2004 | Horizon Worlds | Virtual billboards, Sponsored events, Avatar branding | Nike, Samsung, Gucci | 1200 |
| Niantic | San Francisco, USA | 2010 | Real-world AR metaverse | Location-based ads, Sponsored AR experiences | McDonald’s, Starbucks | 350 |
| Decentraland | Buenos Aires, Argentina | 2017 | Decentraland Platform | Virtual land ads, Event sponsorships | Samsung, Atari | 45 |
| The Sandbox | Hong Kong | 2012 | The Sandbox Platform | Virtual real estate ads, Branded experiences | Adidas, Warner Music | 60 |
| Unity Ads | San Francisco, USA | 2004 | Unity Engine Metaverse Games | In-game ads, Interactive ads | Electronic Arts, Zynga | 500 |
The metaverse is an evolving concept, and its advertising landscape will continue to adapt. Metaverse advertising companies are at the forefront of this evolution, continuously exploring new frontiers.
Interoperability and Open Standards
The fragmented nature of the current metaverse presents challenges for advertisers. The development of open standards and greater interoperability between virtual worlds is a significant area of focus.
- Seamless Asset Transfer: The ability for virtual assets, such as avatar wearables, to move freely between different metaverse platforms would simplify campaign management and extend reach. This would reduce the need for creating bespoke assets for each platform.
- Unified Identity Systems: A single, persistent user identity across multiple metaverses would enable more consistent tracking of user behavior and preferences, simplifying personalization efforts for advertisers.
- Standardized Data Formats: Adopting common data formats for analytics and user data across platforms would allow for more comprehensive campaign analysis and optimization.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize how advertising is created, delivered, and optimized in the metaverse.
- Personalized Virtual Experiences: AI can analyze user behavior and preferences to dynamically generate personalized virtual environments or tailor ad content in real-time. This could lead to highly targeted and relevant advertising experiences.
- Automated Content Creation: AI-powered tools could automate aspects of 3D asset generation, reducing development costs and accelerating campaign deployment. Brands could generate variations of virtual products or environments with minimal manual effort.
- Predictive Analytics: ML algorithms can predict user behavior within the metaverse, helping advertisers to place assets strategically, time events optimally, and anticipate trends.
Ethical Considerations and Regulation
As metaverse advertising becomes more sophisticated, ethical considerations and regulatory frameworks will become increasingly important. Companies in this space also provide guidance on navigating this complex terrain.
- Data Privacy and Security: Protecting user data in highly immersive and persistent virtual environments will require robust privacy policies and compliance with evolving regulations like GDPR. The scope of data collection and its usage will need clear disclosures.
- Truth in Advertising: Ensuring that virtual representations of products and services are accurate and not misleading. The line between real and virtual can blur, necessitating clear distinctions.
- Child Protection: Implementing safeguards to protect younger users from inappropriate content or exploitative advertising practices, especially given the prevalence of younger demographics on some metaverse platforms. This includes age verification and content moderation.
- Virtual World Governance: Addressing issues of ownership, intellectual property, and moderation within decentralized virtual environments. Advertisers need to understand the rules and codes of conduct of the metaverses they operate within.
The metaverse represents a transformative shift in digital interaction, and advertising companies are adapting to this new medium. Their role is to bridge the strategic needs of brands with the technical and creative possibilities of virtual worlds, helping clients navigate a rapidly evolving landscape.









Leave a Reply