The concept of a metaverse, often envisioned as a persistent, interconnected set of virtual spaces, has gained significant traction. This article explores “Metaverse Zukunft: The Future of Virtual Reality,” examining its foundational concepts, technological underpinnings, potential applications, challenges, and societal implications. We will assess the trajectory of virtual reality (VR) and its role in shaping this evolving digital frontier.
The metaverse is not a singular entity but rather a spectrum of interoperable virtual environments. It represents a potential evolution of the internet, transitioning from discrete websites to immersive, persistent digital worlds. This concept draws variously from science fiction, particularly Neal Stephenson’s Snow Crash, and the ongoing development of immersive technologies.
Defining Key Terms
To understand the metaverse, one must first grasp its constituent elements.
Virtual Reality (VR)
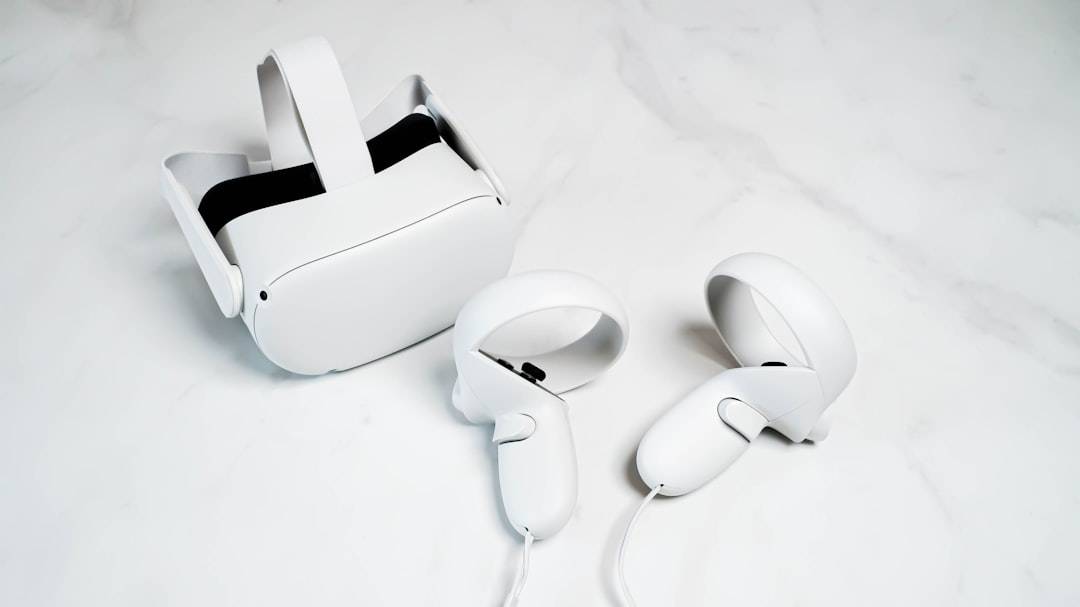
VR denotes an artificial, computer-generated environment that simulates physical presence. It typically employs specialized hardware, such as head-mounted displays, to immerse users. This immersion often includes visual, auditory, and sometimes haptic feedback, creating a sense of being “in” the digital world.
Augmented Reality (AR)
AR overlays digital information onto the real world. Unlike VR, which creates an entirely artificial environment, AR enhances the user’s perception of reality. Examples include smartphone applications that superimpose digital imagery onto live camera feeds or specialized glasses that display notifications in the user’s field of vision.
Mixed Reality (MR)
MR represents a hybrid of VR and AR. It involves the merging of real and virtual worlds to produce new environments and visualizations where physical and digital objects coexist and interact in real time. MR devices often allow for interaction with both real and virtual elements within the same field of view.
Historical Precedents
The idea of virtual worlds predates modern computing. Early forms of virtual environments can be traced back to flight simulators and sensorama machines in the mid-20th century. The development of graphical user interfaces and online multiplayer games further paved the way for more sophisticated digital interactions. The 2000s saw the rise of virtual worlds like Second Life, which offered users customizable avatars and persistent social spaces, laying crucial groundwork for contemporary metaverse discussions.
The concept of the Metaverse continues to evolve, and for those interested in exploring its future potential, a related article titled “What is the Metaverse?” provides valuable insights. This article delves into the various aspects of the Metaverse, including its definition, applications, and the technology driving its development. To read more about this fascinating topic, visit What is the Metaverse?.
Technological Pillars
The realization of a robust metaverse hinges on advances across multiple technological domains. These pillars act as the structural supports for this digital edifice.
Computing Power and Cloud Infrastructure
The rendering of complex virtual environments and the processing of vast amounts of data generated by user interactions demand significant computing power. Cloud computing plays a critical role here, providing scalable resources to host and manage these persistent digital spaces. This distributed infrastructure allows for the global accessibility and continuous operation of metaverse platforms.
Connectivity and Bandwidth
A seamless metaverse experience requires high-speed, low-latency internet connectivity. Technologies like 5G are crucial for enabling real-time interactions, streaming high-fidelity graphics, and supporting a multitude of concurrent users. Without adequate bandwidth, the metaverse would remain a series of disconnected, lag-prone experiences.
Interoperability and Standards
One of the central tenets of the metaverse concept is interoperability – the ability for assets, identities, and experiences to move freely between different virtual platforms. This requires the development and adoption of open standards for data formats, digital asset ownership (e.g., NFTs), and identity management. Without such standards, the metaverse risks fragmenting into isolated, proprietary ecosystems.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML will underpin various metaverse functionalities. This includes generating realistic in-world content, personalizing user experiences, powering intelligent non-player characters (NPCs), and moderating content. AI can also facilitate more natural user interfaces through natural language processing and advanced computer vision.
Blockchain and Digital Ownership
Blockchain technology offers a mechanism for verifiable digital ownership. Non-fungible tokens (NFTs), built on blockchain, allow for unique digital assets to be owned and traded within the metaverse, from virtual clothing to digital land. This technology could provide a foundation for a digital economy within these virtual spaces, fostering scarcity and value.
Potential Applications and Use Cases
The metaverse promises a wide array of applications, extending beyond mere entertainment. It has the potential to transform how we work, learn, socialize, and consume.
Social Interaction and Community Building
The metaverse offers new avenues for social interaction, enabling users to meet, communicate, and collaborate in immersive 3D environments. This could range from casual hangouts to large-scale virtual events like concerts or conferences, transcending geographical barriers.
Education and Training
Immersive VR environments can provide highly effective educational and training platforms. Students could virtually dissect a human body, explore ancient civilizations, or conduct scientific experiments without physical limitations. Professionals could undergo realistic simulations for complex procedures, such as surgical training or emergency response.
Commerce and Digital Economies
The metaverse presents a burgeoning landscape for digital commerce. Users can browse virtual storefronts, purchase digital goods (e.g., avatar clothing, virtual furniture), and engage in virtual services. The integration of blockchain technology facilitates new economic models and decentralized marketplaces within these environments.
Enterprise and Collaboration
Businesses are exploring the metaverse for enhanced collaboration and remote work. Virtual meeting spaces can offer a more engaging and productive alternative to traditional video conferencing. Companies can also use the metaverse for product design, prototyping, and showcasing, allowing stakeholders to interact with 3D models in a shared virtual space.
Entertainment and Gaming
Gaming is a natural fit for the metaverse. Existing online multiplayer games are already precursors to what a fully integrated metaverse could offer. Beyond gaming, virtual concerts, interactive storytelling, and immersive cinematic experiences represent significant entertainment opportunities.
Challenges and Roadblocks
Despite its potential, the development and widespread adoption of the metaverse face considerable obstacles. It is not merely a matter of technological capability but also of social and ethical considerations.
Technical Limitations
Current VR hardware, while advancing, still presents limitations in terms of resolution, field of view, comfort, and cost. Furthermore, creating truly realistic and extensive virtual worlds requires immense computational resources and sophisticated content creation pipelines. The “uncanny valley” effect, where digital representations appear nearly human but subtly off-putting, remains a challenge for realistic avatar creation.
Interoperability and Open Standards
As noted earlier, the lack of widespread interoperability standards is a significant hurdle. Without them, the metaverse could splinter into proprietary walled gardens, limiting the seamless flow of users and assets. Achieving consensus among competing technology companies on common protocols remains a complex task.
Privacy and Data Security
Entering the metaverse implies generating vast amounts of personal data, including biometric data from VR headsets, behavioral patterns, and social interactions. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is paramount. The potential for surveillance, data breaches, and misuse of personal information presents serious ethical and regulatory challenges.
Digital Identity and Governance
Managing digital identities within a decentralized and persistent virtual world raises questions of authenticity, ownership, and reputation. Establishing effective governance structures, both technical and social, to manage disputes, enforce rules, and protect users within the metaverse will be crucial. This includes addressing issues of harassment, misinformation, and digital property rights.
Accessibility and Inclusivity
The metaverse, in its current iterations, often requires expensive hardware, specialized skills, and robust internet access. This creates potential barriers to entry, exacerbating existing digital divides. Ensuring that the metaverse is accessible and inclusive to a diverse global population is essential to avoid creating a new form of digital elitism.
Mental Health and Addiction
The immersive nature of VR and the persistence of virtual worlds raise concerns about potential negative impacts on mental health. Excessive engagement could lead to social isolation in the physical world, addiction, and a blurring of lines between reality and virtuality. Research into these long-term psychological effects is ongoing and necessary.
As the concept of the Metaverse continues to evolve, exploring its various platforms and ecosystems becomes increasingly important for understanding its future. A related article discusses the intricacies of social virtual worlds and how they contribute to the overall landscape of the Metaverse. For more insights on this topic, you can read the article on Metaverse platforms and ecosystems, which delves into the different dimensions of these digital environments and their potential impact on society.
Societal Implications
| Metric | Value | Unit | Year | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Global Metaverse Market Size | 800 | Billion | 2028 | Projected market value |
| Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) | 40 | Percent | 2023-2028 | Compound annual growth rate |
| Number of Active Metaverse Users | 500 | Million | 2025 | Estimated active users worldwide |
| Investment in Metaverse Technologies | 120 | Billion | 2024 | Global investment amount |
| VR/AR Device Adoption Rate | 25 | Percent | 2026 | Percentage of population using VR/AR devices |
| Enterprise Adoption Rate | 60 | Percent | 2027 | Percentage of enterprises using metaverse solutions |
The emergence of a ubiquitous metaverse has far-reaching societal implications, impacting everything from economics to human interaction. It is a nascent landscape, and its ultimate form is yet to be fully defined.
Economic Shifts and New Markets
The metaverse is poised to foster entirely new economic models and industries. Virtual real estate, digital fashion, avatar customization services, and NFT marketplaces are already demonstrating significant economic activity. This could lead to new job categories and shifts in existing labor markets.
Evolution of Human Interaction
The metaverse could profoundly alter how humans interact. While offering new avenues for connection, it also raises questions about the nature of human relationships forged primarily in virtual spaces. The distinction between online and offline identities could become increasingly fluid.
Legal and Ethical Frameworks
Current legal and ethical frameworks were largely developed for a physical, geographically defined world. The metaverse, existing beyond traditional borders and physical constraints, will necessitate new legal and ethical considerations regarding jurisdiction, intellectual property, censorship, and accountability within virtual environments.
The Blurring of Realities
As VR and AR technologies advance, the line between physical and digital realities may become increasingly blurred. This could lead to philosophical debates about the nature of reality, personal identity, and the value we assign to experiences in the physical versus virtual worlds. It is akin to stepping through a portal, where the landscape on the other side might eventually become as familiar as the one we left behind.
Conclusion
“Metaverse Zukunft: The Future of Virtual Reality” is not a singular, predetermined destination but rather a dynamic and evolving journey. The metaverse, underpinned by continuous advancements in VR, AR, AI, and connectivity, holds significant potential to reshape various aspects of human experience. However, its development is accompanied by substantial technical, ethical, and societal challenges. Overcoming these hurdles will require collaborative efforts from technologists, policymakers, academics, and users. The trajectory of this digital frontier will ultimately be shaped by how effectively these challenges are addressed and how thoughtfully its potential is harnessed to create a future that is inclusive, beneficial, and sustainable. The choices made today in developing its infrastructure, crafting its rules, and defining its purpose will determine whether the metaverse becomes a tool for human flourishing or a complex new domain of concern.









Leave a Reply