In recent years, the intersection of artificial intelligence (AI) and wildlife conservation has emerged as a groundbreaking frontier in environmental science. As the world grapples with the alarming decline of biodiversity, innovative technologies are being harnessed to monitor and protect endangered species. AI-based wildlife monitoring systems are at the forefront of this movement, utilizing advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze vast amounts of data collected from various sources, including camera traps, drones, and acoustic sensors.
This technological revolution not only enhances our understanding of wildlife behavior but also empowers conservationists to make informed decisions that can significantly impact the survival of vulnerable species. The integration of AI into wildlife monitoring represents a paradigm shift in how we approach conservation efforts. Traditional methods often relied on manual observation and data collection, which were time-consuming and limited in scope.
However, with the advent of AI, researchers can now process and analyze data at an unprecedented scale and speed. This capability allows for real-time monitoring of animal populations, habitat usage, and even behavioral patterns, providing invaluable insights that were previously unattainable. As we delve deeper into the significance of monitoring rare and endangered species, it becomes clear that AI is not just a tool; it is a vital ally in the fight against extinction.
Key Takeaways
- AI-based wildlife monitoring uses advanced technology to track and analyze animal behavior in their natural habitats.
- Monitoring rare and endangered species is crucial for conservation efforts and AI systems can help in identifying and protecting these vulnerable animals.
- AI systems analyze images and sensor data by using algorithms to detect and classify animals, helping researchers to gather valuable information about wildlife populations.
- Case studies have shown successful automatic animal recognition in wilderness cameras, demonstrating the potential of AI in wildlife monitoring.
- The benefits of using AI for wildlife monitoring include improved efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness in data collection and analysis.
The importance of monitoring rare and endangered species
Importance of Monitoring Rare and Endangered Species
Monitoring rare and endangered species is crucial for several reasons, primarily centered around the preservation of biodiversity and the health of ecosystems. These species often play critical roles in their habitats, contributing to ecological balance and resilience. For instance, apex predators help regulate prey populations, while pollinators are essential for plant reproduction.
The Consequences of Species Loss
The loss of any single species can trigger a cascade of negative effects throughout the ecosystem, leading to further declines in biodiversity. Therefore, understanding the status and trends of these species is essential for effective conservation strategies. Moreover, monitoring provides essential data that informs policy decisions and conservation actions.
Targeted Conservation Efforts
By tracking population dynamics, habitat use, and threats faced by endangered species, conservationists can develop targeted interventions that address specific challenges. For example, if a particular species is found to be declining due to habitat loss or poaching, conservation efforts can be directed towards habitat restoration or anti-poaching initiatives.
The Role of AI-Based Monitoring Systems
In this context, AI-based monitoring systems offer a powerful solution by enabling continuous data collection and analysis, ensuring that conservationists have access to timely information that can guide their efforts.
How AI systems analyze images and sensor data
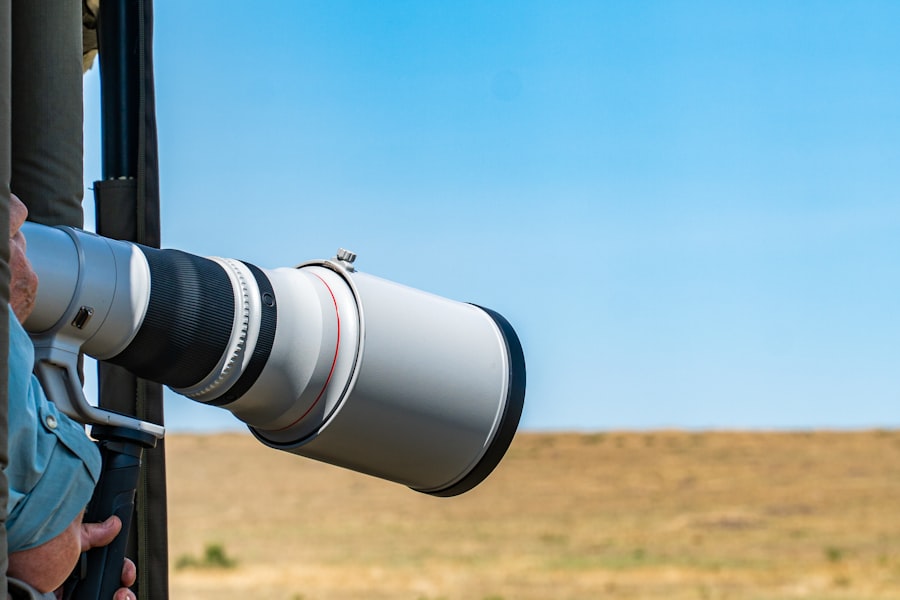

AI systems employed in wildlife monitoring utilize sophisticated algorithms to analyze images and sensor data collected from various sources. One of the most common applications involves the use of computer vision techniques to process images captured by camera traps. These cameras are strategically placed in natural habitats to capture photographs or videos of wildlife as they pass by.
Once the images are collected, AI algorithms can be trained to recognize specific species based on their physical characteristics, such as size, shape, color patterns, and even behavioral traits. Machine learning models are particularly effective in this context because they can learn from vast datasets and improve their accuracy over time. Initially, researchers may manually label images to create a training dataset that includes various species.
The AI system then uses this dataset to learn the distinguishing features of each species. As more images are processed, the model becomes increasingly adept at identifying animals in new images, even those it has never encountered before. This capability not only streamlines the identification process but also reduces human error and bias, leading to more reliable data on wildlife populations.
In addition to image analysis, AI systems can also process data from acoustic sensors that capture sounds made by animals in their natural habitats. By employing techniques such as sound classification and pattern recognition, AI can identify specific calls or vocalizations associated with different species. This multimodal approach—combining visual and auditory data—enhances the overall understanding of wildlife behavior and interactions within ecosystems.
Case studies of automatic animal recognition in wilderness cameras
Several case studies illustrate the successful application of AI-based automatic animal recognition in wilderness cameras, showcasing its potential for advancing wildlife monitoring efforts. One notable example comes from a project conducted in the Amazon rainforest, where researchers deployed camera traps equipped with AI algorithms to monitor jaguar populations. By analyzing thousands of images captured over several months, the AI system was able to identify individual jaguars based on unique spot patterns on their fur.
This information allowed researchers to estimate population density and track movement patterns across different regions of the rainforest. Another compelling case study took place in Africa’s Serengeti National Park, where scientists utilized AI-powered camera traps to monitor large herbivores such as elephants and wildebeests. The system was designed to differentiate between species based on size and shape while also recognizing individual animals through unique physical features.
These case studies not only demonstrate the effectiveness of AI in recognizing animals but also highlight its potential for large-scale conservation efforts. By automating the identification process, researchers can focus their time and resources on analyzing trends and implementing conservation strategies rather than spending countless hours sifting through images manually.
The benefits of using AI for wildlife monitoring
The benefits of employing AI for wildlife monitoring are manifold, significantly enhancing both efficiency and effectiveness in conservation efforts. One of the most significant advantages is the ability to process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately. Traditional methods often involve labor-intensive manual analysis, which can lead to delays in obtaining critical information about wildlife populations.
In contrast, AI systems can analyze thousands of images or sound recordings within minutes, providing real-time insights that enable timely decision-making. Additionally, AI-based monitoring systems can operate continuously without fatigue or bias. Unlike human observers who may miss subtle cues or become fatigued during long hours of observation, AI algorithms maintain consistent performance over extended periods.
This reliability ensures that no critical data points are overlooked, leading to a more comprehensive understanding of wildlife dynamics. Furthermore, as these systems learn from new data inputs over time, their accuracy improves, resulting in increasingly precise monitoring capabilities. Another notable benefit is the cost-effectiveness associated with AI technologies.
While initial investments in camera traps and sensor networks may be substantial, the long-term savings realized through reduced labor costs and increased efficiency can be significant. Moreover, by enabling more effective conservation strategies based on accurate data, AI can ultimately lead to better outcomes for endangered species and their habitats.
Challenges and limitations of AI-based animal detection
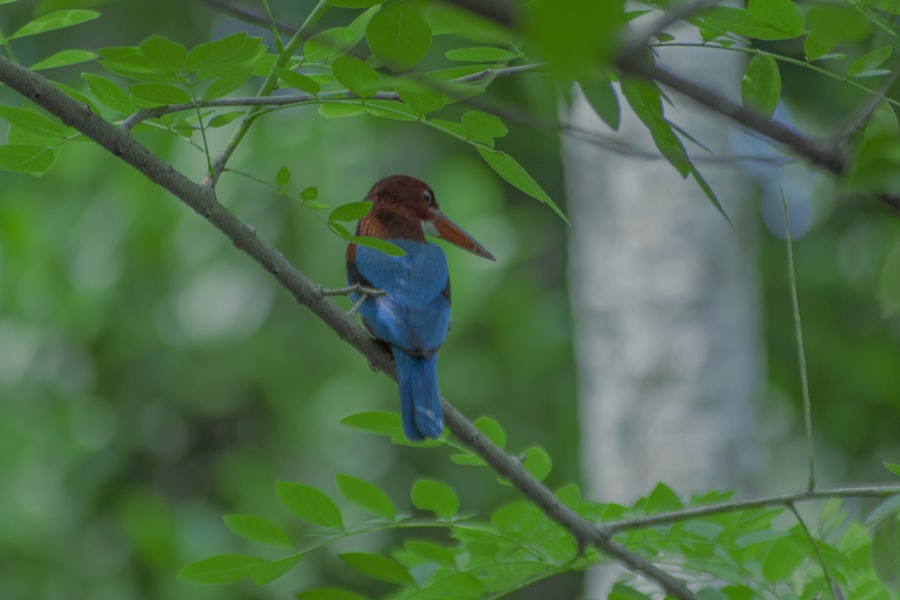

Despite its numerous advantages, AI-based animal detection is not without challenges and limitations that must be addressed for optimal effectiveness in wildlife monitoring. One primary concern is the quality and representativeness of training datasets used to develop machine learning models. If the training data is biased or lacks diversity—such as being skewed towards certain species or geographic regions—the resulting model may perform poorly when applied to new environments or less-represented species.
Ensuring that datasets are comprehensive and representative is crucial for developing robust AI systems capable of accurately identifying a wide range of animals. Another challenge lies in the potential for false positives or negatives during animal detection processes. While AI algorithms have made significant strides in accuracy, they are not infallible.
These inaccuracies can lead to misleading conclusions about population sizes or distribution patterns if not carefully monitored and validated against ground-truth data. Additionally, ethical considerations surrounding privacy and data collection must be taken into account when deploying AI technologies in natural habitats.
The use of camera traps raises questions about potential intrusions into wildlife privacy and the implications for animal behavior when they become aware of surveillance devices. Striking a balance between effective monitoring and ethical considerations is essential for maintaining public support for conservation initiatives.
Future developments and potential applications in conservation projects
Looking ahead, the future developments in AI-based wildlife monitoring hold immense promise for enhancing conservation projects worldwide. As technology continues to advance, we can expect improvements in algorithmic sophistication that will enable even more accurate species identification and behavioral analysis. For instance, integrating deep learning techniques with real-time data processing could allow researchers to monitor animal movements dynamically as they occur rather than relying solely on post-hoc analysis.
Moreover, the potential applications of AI extend beyond traditional wildlife monitoring scenarios. For example, combining AI with satellite imagery could facilitate large-scale habitat assessments by identifying changes in land use or vegetation cover over time. This capability would enable conservationists to respond proactively to threats such as deforestation or urban encroachment before they escalate into more significant issues.
Furthermore, collaborative efforts between technology companies and conservation organizations could lead to innovative solutions tailored specifically for wildlife protection. Initiatives such as open-source platforms for sharing datasets or developing user-friendly interfaces for non-experts could democratize access to advanced monitoring tools, empowering local communities to engage actively in conservation efforts.
the potential of AI in supporting wildlife conservation efforts
In conclusion, the integration of artificial intelligence into wildlife monitoring represents a transformative advancement in conservation science. By harnessing the power of machine learning algorithms and data analytics, researchers can gain unprecedented insights into animal populations and behaviors while streamlining data collection processes. The importance of monitoring rare and endangered species cannot be overstated; it is essential for preserving biodiversity and ensuring healthy ecosystems.
While challenges remain—such as ensuring data quality and addressing ethical considerations—the potential benefits far outweigh these obstacles. As technology continues to evolve, so too will our ability to protect vulnerable species from extinction through informed decision-making based on accurate data analysis. Ultimately, AI stands as a powerful ally in our ongoing efforts to safeguard wildlife for future generations—a testament to human ingenuity working hand-in-hand with nature’s wonders.
Leider scheint keiner der angegebenen Links direkt mit dem Thema KI-basierte Erfassung von Tieren in der Wildnis zusammenzuhängen. Diese Links beziehen sich hauptsächlich auf das Metaversum und dessen soziale sowie wirtschaftliche Auswirkungen. Für spezifischere Informationen zur Anwendung von KI-Systemen in der Tierbeobachtung und im Naturschutz wäre es ratsam, nach spezialisierten Artikeln oder Berichten zu suchen, die sich direkt mit dieser Technologie und deren Einsatz in der Wildtierforschung befassen.
FAQs
What is KI-basierte Erfassung von Tieren in der Wildnis?
KI-basierte Erfassung von Tieren in der Wildnis refers to the use of artificial intelligence (KI) systems to analyze images or sensor data in order to identify and track rare or endangered animal species in their natural habitat. This technology can support conservation efforts and wildlife monitoring projects.
How do KI systems help in automatic animal recognition in wildlife cameras?
KI systems can be trained to recognize specific animal species by analyzing patterns and features in images captured by wildlife cameras. By using machine learning algorithms, these systems can learn to identify and classify different animals, allowing for automatic detection and recognition of rare or endangered species in the wild.
What are the applications of KI-basierte Erfassung von Tieren in der Wildnis?
The applications of KI-basierte Erfassung von Tieren in der Wildnis include automatic animal recognition in wildlife cameras, monitoring of wildlife populations, tracking of animal movements, and supporting conservation efforts by identifying and protecting rare or endangered species.
How do KI systems support nature conservation projects?
KI systems support nature conservation projects by providing a non-invasive and efficient method for monitoring wildlife populations and identifying rare or endangered species. This information can be used to inform conservation strategies, protect habitats, and support efforts to preserve biodiversity.
What are the benefits of using KI-basierte Erfassung von Tieren in der Wildnis?
The benefits of using KI-basierte Erfassung von Tieren in der Wildnis include improved efficiency and accuracy in wildlife monitoring, non-invasive data collection, support for conservation efforts, and the ability to track and protect rare or endangered animal species in their natural habitat.









Leave a Reply