The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into robotic surgery represents a transformative leap in the field of medicine, merging cutting-edge technology with the precision of surgical procedures. As healthcare continues to evolve, the incorporation of AI into robotic systems is not merely an enhancement; it is a revolution that promises to redefine surgical practices. Surgeons are now equipped with tools that not only augment their capabilities but also provide insights that were previously unattainable.
This synergy between human expertise and machine intelligence is paving the way for safer, more efficient, and highly personalized surgical interventions. Robotic surgery has already made significant strides, with systems like the da Vinci Surgical System leading the charge. However, the infusion of AI into these platforms is what truly sets the stage for a new era.
By harnessing vast amounts of data and employing machine learning algorithms, AI can analyze surgical patterns, predict outcomes, and even assist in real-time decision-making during procedures. This article delves into the multifaceted role of AI in robotic surgery, exploring its impact on preoperative planning, intraoperative decision-making, postoperative care, and the ethical considerations that accompany these advancements.
Key Takeaways
- AI plays a crucial role in robotic surgery by assisting surgeons in preoperative planning, intraoperative decision making, and postoperative care.
- AI helps in preoperative planning by analyzing patient data to create personalized surgical plans, leading to more precise and efficient procedures.
- Intraoperatively, AI provides real-time feedback and guidance to surgeons, improving decision making and enhancing surgical outcomes.
- Advancements in surgical instrumentation and robotics, driven by AI, have led to the development of more sophisticated and precise tools for minimally invasive procedures.
- AI contributes to postoperative care and recovery by analyzing patient data to personalize rehabilitation plans and improve long-term outcomes.
The Role of AI in Preoperative Planning
Personalized Surgical Plans
By analyzing patient data, including medical history, imaging studies, and even genetic information, AI algorithms can identify potential complications and suggest optimal surgical approaches. This data-driven insight allows surgeons to make informed decisions that enhance patient safety and improve overall surgical efficacy.
VIRTUAL SIMULATION AND PRACTICE
Moreover, AI can simulate various surgical scenarios based on the unique anatomy of each patient. These simulations provide surgeons with a virtual environment to practice and refine their techniques before entering the operating room.
Improved Outcomes and Reduced Recovery Times
This not only boosts the surgeon’s confidence but also minimizes the risk of unforeseen challenges during the actual procedure. As a result, preoperative planning becomes a more dynamic and interactive process, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and reduced recovery times.
AI’s Impact on Intraoperative Decision Making
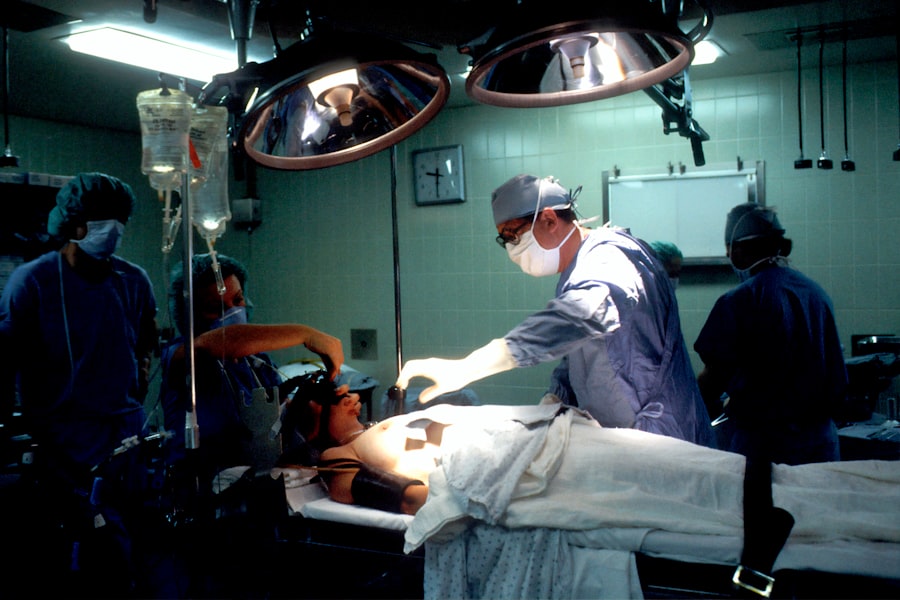
During surgery, the ability to make quick and accurate decisions is paramount. AI’s role in intraoperative decision-making is becoming increasingly significant as it provides real-time data analysis and predictive insights. Advanced imaging technologies combined with AI algorithms can offer surgeons enhanced visualization of the surgical site, highlighting critical structures and potential risks.
This augmented reality approach allows for a more precise navigation of complex anatomical landscapes, reducing the likelihood of errors. Furthermore, AI systems can monitor vital signs and other physiological parameters during surgery, alerting the surgical team to any deviations from expected norms.
This level of support not only enhances patient safety but also empowers surgeons to focus on their primary task—performing the surgery—while relying on AI to manage ancillary concerns.
Advancements in Surgical Instrumentation and Robotics
The evolution of surgical instrumentation has been significantly influenced by advancements in robotics and AI. Modern robotic systems are equipped with sophisticated tools that allow for greater dexterity and precision than traditional methods. These instruments can perform intricate movements with unparalleled accuracy, minimizing tissue damage and promoting faster recovery times.
The integration of AI into these robotic systems further enhances their capabilities by enabling adaptive learning from each procedure. For instance, some robotic systems are now capable of adjusting their movements based on real-time feedback from the surgical environment. This adaptability allows for a more responsive approach to surgery, where instruments can modify their actions based on the surgeon’s techniques or unexpected anatomical variations encountered during the procedure.
Such innovations not only improve surgical outcomes but also expand the range of procedures that can be performed robotically.
AI’s Contribution to Postoperative Care and Recovery
The role of AI does not end once the surgery is completed; it extends into postoperative care and recovery as well. AI-driven platforms can monitor patients’ recovery progress through wearable devices that track vital signs and other health metrics. By analyzing this data, AI can identify potential complications early on, allowing healthcare providers to intervene promptly.
This proactive approach to postoperative care significantly enhances patient safety and reduces hospital readmission rates. Additionally, AI can facilitate personalized recovery plans tailored to each patient’s unique needs. By considering factors such as age, medical history, and individual responses to surgery, AI algorithms can recommend specific rehabilitation exercises or lifestyle modifications that optimize recovery outcomes.
This level of customization ensures that patients receive the most effective care possible, ultimately leading to improved quality of life post-surgery.
Challenges and Limitations of AI in Robotic Surgery
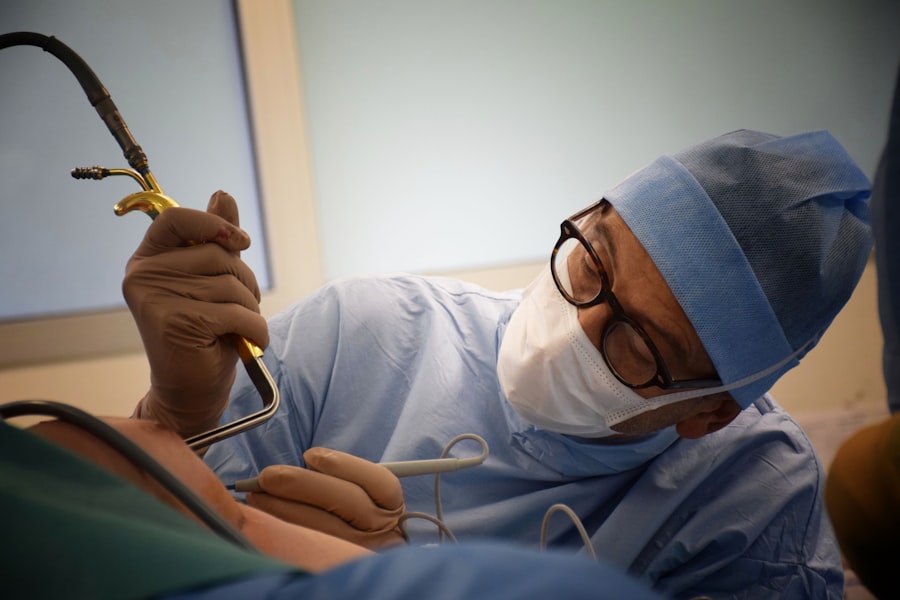
Data Quality and Availability
AI algorithms are only as good as the data they are trained on; if this data is incomplete or biased, it can lead to inaccurate predictions or recommendations. Ensuring that diverse and comprehensive datasets are used for training is crucial for minimizing these risks.
Acceptance and Trust Among Healthcare Professionals
Another challenge lies in the acceptance and trust of AI among healthcare professionals. Surgeons may be hesitant to rely on machine-generated insights, fearing that it could undermine their expertise or lead to errors in judgment.








Leave a Reply